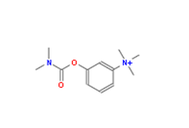
Neostigmine is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention
Neostigmine is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used together with atropine to end the effects of neuromuscular blocking medication of the non-depolarizing type. It is given by injection either into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. After injection effects are generally greatest within 30 minutes and last up to 4 hours.
Common side effects include nausea, increased saliva, crampy abdominal pain, and slow heart rate. More severe side effects include low blood pressure, weakness, and allergic reactions. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Neostigmine is in the cholinergic family of medications. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase and therefore increases the levels of acetylcholine.
Neostigmine was patented in 1931. It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. The term is from Greek neos, meaning “new”, and “-stigmine”, in reference to its parent molecule, physostigmine, on which it is based.